The Complete Timeline for Transitioning from In-House to Outsourced Accounting
- Nitin Punera

- Apr 1, 2025
- 8 min read
Is your in-house accounting team stretched thin?
You’re not alone.
Many accounting firms struggle with tight reporting deadlines, rising costs, and constant regulatory changes. As client demands increase, firms with limited in-house capacity often face scalability issues. That’s why understanding the outsourced accounting transition timeline is crucial for maintaining service quality while expanding efficiently.
Outsourced accounting isn’t just for large firms—it’s an effective strategy for small and mid-sized accounting practices looking to improve efficiency, reduce operational burdens, and focus on high-value services like advisory and tax planning.
In fact, 73% of UK accountants recognize the positive impact of outsourcing, enabling firms to allocate more time to strategic functions rather than routine compliance work. Additionally, nearly 40% of small to medium-sized firms plan to increase their use of outsourcing to remain competitive.
The UK’s outsourcing market continues to expand, with business process outsourcing projected to reach £21.8 billion by 2025. For accounting firms, leveraging external partners is no longer an option but a necessity for sustainable growth.
In this blog, you’ll learn:
Why outsourcing makes sense for accounting firms
How to assess if it’s right for your firm
The step-by-step transition process
Which tasks you should consider outsourcing
Common mistakes to avoid
How to choose the right outsourcing partner
We’ll walk you through each stage to ensure a smooth transition. Let’s get started!
Why Consider Outsourced Accounting? Understanding the Outsourced Accounting Transition Timeline
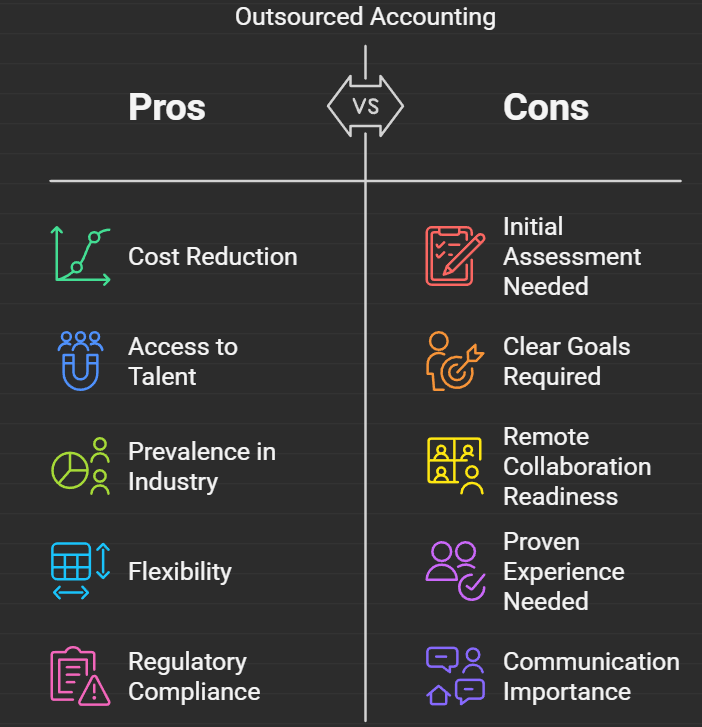
Outsourcing isn’t just about cost savings—it’s about improving service delivery, increasing capacity, and staying ahead of industry shifts.
Here’s how your firm benefits:
Cost Efficiency – Accounting firms can reduce operational costs by 30% to 50% by outsourcing tasks like bookkeeping, payroll processing, and compliance work.
Industry Trends – Nearly 70% of B2B firms in the UK outsource key functions, with 37% outsourcing accounting-related tasks, reflecting a shift toward external expertise.
Scalability – Firms can scale resources up or down based on client demand, avoiding the inefficiencies of idle staff.
Hiring Costs & Efforts – Outsourcing reduces the time, effort, and expenses associated with recruiting, training, and retaining skilled accounting professionals.
Regulatory Compliance – Outsourcing providers stay updated on evolving regulations, reducing compliance risks and potential penalties.
Initial Assessment: Is Outsourcing Right for Your Firm?
Before making the transition, assess whether outsourcing aligns with your firm’s goals and current challenges.
Step 1: Evaluate Your Current Setup
Identify inefficiencies like missed deadlines, high staff workloads, or compliance issues. If your firm is struggling with resource constraints, outsourcing could provide the support needed to maintain high service levels.
Step 2: Define Clear Objectives
Set specific outsourcing goals—whether it’s reducing costs, improving accuracy, or increasing capacity for advisory services. Establish KPIs like turnaround times and accuracy rates to measure success.
Step 3: Assess Remote Collaboration Readiness
Ensure your firm is equipped for virtual collaboration. Secure cloud-based tools and a structured onboarding process will help facilitate a smooth transition.
Choosing the Right Outsourcing Partner
Here’s how to choose wisely:
1. Experience with Accounting Firms
Look for an outsourcing provider that specializes in supporting accounting firms. They should understand your workflow, client expectations, and compliance requirements.
2. Technical Expertise & Capacity
Ensure the outsourced team has relevant qualifications and experience in areas like tax compliance, bookkeeping, and financial reporting. They should also have the capacity to scale as your firm grows.
3. Communication & Culture Fit
Seamless communication is key. The provider should offer regular updates, structured reporting, and proactive issue resolution. A cultural fit with your firm’s working style is equally important.
4. Value Over Cost
While affordability matters, choosing the lowest-cost provider may compromise service quality. Focus on expertise, reliability, and client testimonials to ensure a strong partnership.
The Transition Process: Step-by-Step
Step 1: Develop a Transition Plan
Before moving forward with outsourcing, it's essential to have a well-defined transition plan.
Define the Scope of Outsourced Tasks: Identify which accounting functions you will outsource, such as bookkeeping, payroll, VAT returns, or financial reporting. Be clear on what remains in-house to avoid duplication or gaps in responsibilities.
Assign Responsibilities Within Your Firm: Designate a point of contact within your firm who will oversee the transition and coordinate with the outsourced team. This ensures accountability and smooth collaboration.
Set Realistic Timelines for the Transition: Establish a timeline for each stage of the transition, ensuring there’s adequate time for testing, adjustments, and troubleshooting. Avoid rushing the process, as it may lead to errors or inefficiencies.
Step 2: Securely Transfer Data
Transferring sensitive financial data is one of the most critical steps in the outsourcing transition. A secure and structured approach is essential to maintain confidentiality and compliance.
Use Encrypted File-Sharing Tools: Utilize secure platforms like Dropbox Business, Google Drive (with encryption), or specialized accounting software with built-in security measures to share sensitive data.
Set Clear Access Permissions: Ensure that only authorized individuals have access to specific files and folders. Assign different permission levels (view-only, edit, admin) to protect confidential information.
Backup All Financial Records Before Migration: Create backups of all accounting files, client records, and reports before initiating data transfer. This serves as a safeguard against accidental loss or corruption during migration.
Step 3: Provide Context & Knowledge
The outsourced team needs a clear understanding of your existing processes to integrate seamlessly into your firm’s workflow.
Document Your Accounting Processes: Create a process manual that outlines workflows, key deadlines, and specific instructions for different accounting tasks. This helps the outsourced team work efficiently.
Share Templates, Samples, and Past Reports: Providing standardized formats ensures consistency in financial reporting. If you have preferred ways of categorizing expenses, reconciling accounts, or presenting financial data, share those details.
Introduce Key Contacts for Seamless Collaboration: Ensure that your in-house team knows who to contact at the outsourced firm for specific issues. Setting up an introductory meeting can help establish a good working relationship.
Step 4: Align Your Internal Team
Your in-house team needs to be prepared for the outsourcing shift to prevent confusion and resistance.
Communicate Changes Clearly to Staff: Explain why the firm is transitioning to outsourced accounting, how it benefits the company, and what to expect during the process. Transparency fosters trust and cooperation.
Define New Roles and Responsibilities: Clarify how duties will be reassigned. For example, if payroll processing is outsourced, your HR team should know their revised role in handling employee records and compliance.
Provide Training on Working with the Outsourced Team: Conduct training sessions to familiarize your staff with the new processes, software, and communication methods that will be used when working with the outsourced team.
Step 5: Establish Communication Routines
A structured communication plan is essential for seamless collaboration and quick problem resolution.
Schedule Regular Check-ins with the Outsourced Team: Weekly or bi-weekly calls ensure alignment on priorities, address concerns, and track progress. This prevents miscommunication and enhances efficiency.
Agree on Report Formats and Delivery Timelines: Define how and when financial reports, reconciliations, and compliance filings will be submitted. Ensure both teams are aligned on deadlines and expectations.
Define an Escalation Process for Urgent Matters: Establish a clear protocol for flagging and addressing urgent issues. For example, if a compliance deadline is at risk, the outsourced team should know whom to contact for an immediate resolution.
Step 6: Go Live & Monitor Performance
The transition should be executed gradually, with continuous monitoring to identify and address issues early.
Start with a Phased Rollout Instead of an All-at-Once Transition: Consider outsourcing one function at a time, such as bookkeeping first, followed by payroll and financial reporting. This allows for smoother adaptation and troubleshooting.
Track Performance Against KPIs: Monitor metrics like report accuracy, turnaround times, and compliance adherence to measure the outsourced team’s effectiveness. Regularly review these KPIs to ensure alignment with your firm’s goals.
Address Issues Promptly to Prevent Operational Disruptions: If discrepancies or process inefficiencies arise, resolve them immediately rather than waiting for scheduled check-ins. Quick intervention prevents minor issues from escalating.
Step 7: Review & Optimize
Even after a successful transition, continuous evaluation and improvements are necessary.
Conduct Periodic Performance Evaluations: Every few months, review the efficiency, accuracy, and responsiveness of the outsourced team. Identify areas for improvement and discuss adjustments with your provider.
Adjust Processes Based on Feedback: Gather input from both your in-house staff and the outsourced team to refine workflows. If a process is inefficient, be open to modifying it for better results.
Focus on Continuous Improvement for Long-Term Efficiency Gains: As your firm grows, your outsourcing needs may change. Regularly assess whether you need to scale services, upgrade tools, or optimize collaboration methods.
By following these steps, accounting firms can successfully transition to an outsourced model while ensuring efficiency, security, and compliance.

What Accounting Firms Can Outsource?
1. Bookkeeping
Bookkeeping is the foundation of financial management, ensuring all transactions are recorded accurately and systematically.
Transaction Recording: Every financial transaction—sales, purchases, expenses, and revenues—is documented in the accounting system. This provides a clear financial trail and supports financial reporting.
Bank Reconciliations: Regularly matching bank statements with accounting records to identify discrepancies, prevent fraud, and maintain accuracy in cash balances.
Ledger Maintenance: Keeping general and subsidiary ledgers up to date, ensuring that assets, liabilities, income, and expenses are properly classified for accurate financial reporting.
2. Accounts Payable & Receivable
Managing incoming and outgoing payments efficiently ensures smooth cash flow and strong financial health.
Invoice Processing: Reviewing, verifying, and recording vendor invoices to ensure timely payments and prevent late fees.
Payment Tracking: Monitoring payments due from customers, issuing reminders, and ensuring timely collections to maintain a steady cash flow.
Credit Control: Assessing customer creditworthiness, setting credit limits, and managing overdue payments to minimize bad debts.
3. Payroll Processing
Ensuring employees are paid correctly and on time while complying with tax regulations.
Wage Calculations & Deductions: Processing salaries, bonuses, overtime, and statutory deductions such as income tax and National Insurance contributions.
HMRC Filings: Submitting payroll-related reports to HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC), including PAYE and Real Time Information (RTI) submissions.
Employee Records Management: Keeping track of employee payroll data, benefits, pensions, and sick leave records to ensure compliance with employment laws.
4. Tax Compliance & Filing
Accurate tax filing ensures compliance and minimizes financial risks.
VAT Returns: Preparing and submitting Value Added Tax (VAT) returns in compliance with Making Tax Digital (MTD) requirements.
Corporation Tax Filings: Calculating and filing corporate tax returns, ensuring businesses take advantage of available deductions and allowances.
Self-Assessments: Assisting individuals, sole traders, and business owners in filing self-assessment tax returns accurately and on time.
5. Financial Reporting
Providing insights into a company’s financial health to support decision-making.
Monthly Management Accounts: Preparing profit and loss statements, balance sheets, and key performance indicator (KPI) reports for ongoing business evaluation.
Year-End Reports: Compiling financial statements for compliance, taxation, and investor reporting at the end of the financial year.
Cash Flow Statements: Tracking cash inflows and outflows to help businesses plan for operational and investment needs.
6. Budgeting & Forecasting
Helping businesses plan for future growth and financial stability.
Financial Modelling: Creating projections based on historical data and market trends to assess future profitability and financial viability.
Performance Monitoring: Tracking actual financial performance against budgets to identify variances and adjust strategies accordingly.
Decision-Support Analysis: Providing data-driven insights to support strategic business decisions, such as expansion plans, cost-cutting measures, and investment opportunities.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them?
1. Lack of Clear Expectations
Without well-defined expectations, outsourcing can lead to misalignment and inefficiencies.
How to Avoid It:
Clearly outline Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that measure success, such as turnaround time, accuracy rates, and cost savings.
Set service level agreements (SLAs) detailing response times, deliverables, and escalation processes.
Maintain regular feedback loops to track progress and address concerns proactively.
2. Choosing the Wrong Partner
Selecting a partner based on price alone can lead to poor service quality and communication issues.
How to Avoid It:
Evaluate the provider’s industry expertise, technical skills, and past client reviews.
Ensure the firm has strong communication protocols and understands your company’s specific needs.
Request a trial period or pilot project to assess their capabilities before committing long-term.
3. Poor Internal Planning
Outsourcing affects internal teams, and resistance can lead to inefficiencies.
How to Avoid It:
Secure internal buy-in by explaining the benefits of outsourcing (cost savings, improved efficiency, reduced workload).
Clearly define new roles and responsibilities to prevent confusion.
Provide training sessions to help employees adapt to working with an outsourced team.
4. Rushing the Transition
Moving too quickly can disrupt workflows and create operational bottlenecks.
How to Avoid It:
Implement outsourcing in phases rather than an immediate full-scale transition.
Begin with non-critical tasks before expanding to core functions.
Regularly review performance and adjust ensure a smooth transition.

Next Steps: Transition with Confidence
Now that you understand the process, it’s time to act. Start with a structured plan, set clear goals, and choose an outsourcing partner that aligns with your firm’s needs.
Looking for expert outsourced accounting support? Accountik specializes in helping accounting firms streamline operations with seamless transitions, secure technology, and dedicated support.
Let’s make your firm more efficient—without the overhead!



Comments